Economy
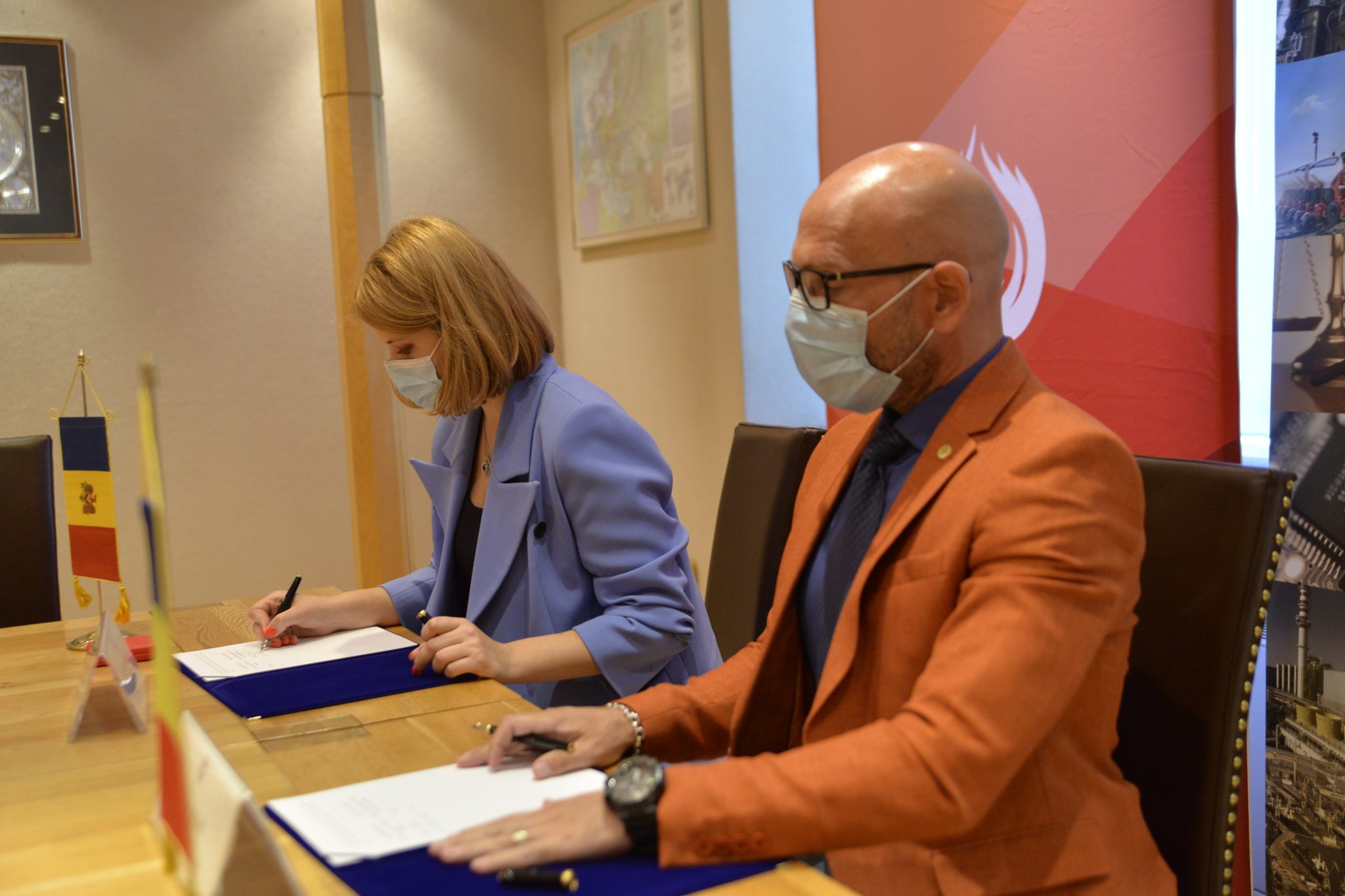
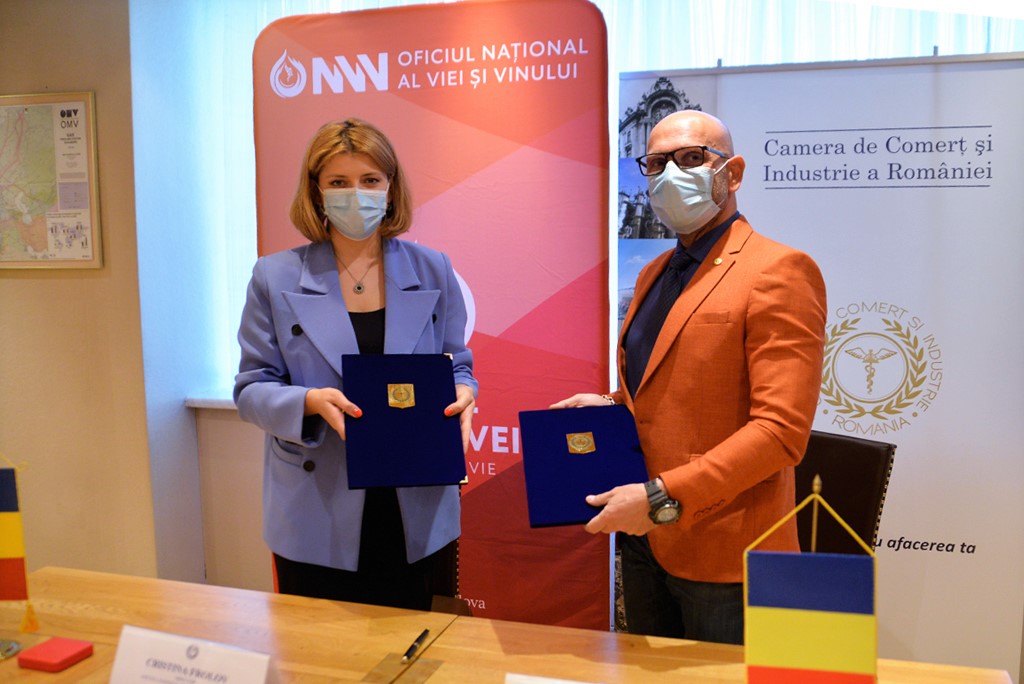
Romania and Moldova signed a partnership memorandum pledging to cooperate in promoting their wines
The Chamber of Commerce and Industry of Romania (CCIR) and the National Office for Vine and Wine (NOVW) of the Republic of Moldova signed, last week, a memorandum of cooperation on organizing joint promotional activities in the markets of common interest, as the CCIR announced.
China, Japan or the USA are just some of the markets targeted by the Romanian and Moldovan institutions. The memorandum also involves advertising activities for wines from common indigenous varieties, promoting the oeno-tourist region, developing a tourist route in the two states, exchange of experience, study visits, and mutual support in identifying new export opportunities. “We are very confident that this collaboration between our organizations will lead to sustainable economic growth and a higher degree of well-being among Moldovans and Romanians,” claimed Deputy Secretary-General of CCIR, Bogdan Visan.
On the other hand, Director of the NOVW, Cristina Frolov, declared that no open competition with Romania is aimed at the governmental level of the Republic of Moldova. “This request for collaboration is a consequence of the partnership principle. Romania imports 10-12% of the wine it consumes, and we want to take more from this import quota. Every year, the Romanian market grows by approximately 2.8%, as it happened in 2020, and we are interested in taking a maximum share of this percentage of imported wines without entering into direct competition with the Romanian producer,” the Moldovan official said. She also mentioned that Moldova aims at increasing the market share of wine production by at least 50% compared to 2020, and the number of producers present on the Romanian market – by at least 40%.

Source: ccir.ro
**
According to the data of the Romanian National Trade Register Office, the total value of Romania-Moldova trade was 1.7 billion euros at the end of last year and over 805 million euros at the end of May 2021. In July 2021, there were 6 522 companies from the Republic of Moldova in Romania, with a total capital value of 45.9 million euros.
The data of Moldova’s National Office of Vine and Wine showed that, in the first 7 months of 2021, the total quantity of bottled wine was about 27 million litres (registering an increase of 10% as compared to the same period last year), with a value of more than one billion lei, which is 32% more than the same period last year. Moldovan wines were awarded 956 medals at 32 international competitions in 2020.
Photo: ccir.ro
Important
#WorldForUkraine – a map that shows the magnitude of the world’s actions against Russian aggression
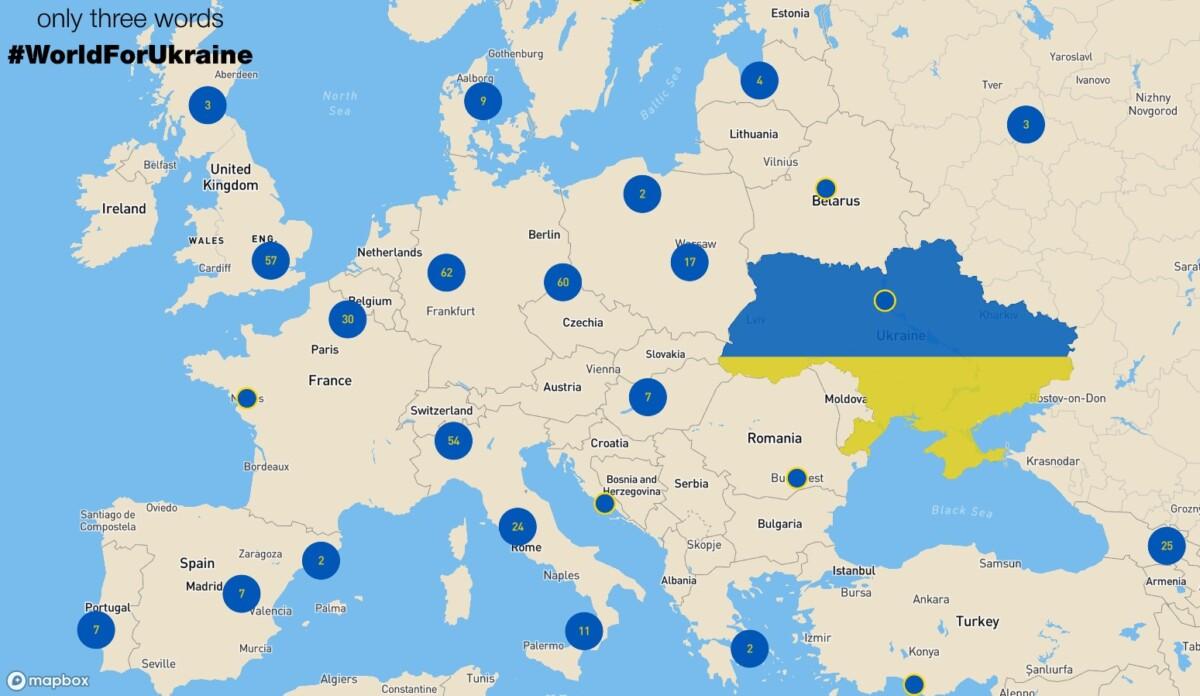
The international community and volunteers from all over te world have launched #WorldForUkraine as a platform that shows the magnitude of the world’s actions against the Russian aggression. In a digital world – it is an interactive map of public support of Ukrainians under the hashtag #WorldForUkraine – rallies, flash mobs, protests around the world. In the physical dimension – it is your opportunity to take to the streets and declare: “No to Putin’s aggression, no to war.”
„Today, along with the political and military support, emotional connection with the civilized world and truthful information are extremely important for Ukraine. The power to do it is in your hands. Join the #WorldForUkraine project and contribute to the victorious battle against the bloodshed inflicted on Ukraine by the aggression of the Russian Federation”, says the „about the project” section of the platform.
Go to the streets — Tell people — Connect and Unite — Become POWERFUL
Volunteers have launched #WorldForUkraine as a platform that shows the magnitude of the world’s actions against Russian aggression. In digital world – it is an INTERACTIVE MAP of public support of Ukrainians worldforukraine.net under the hashtag #WorldForUkraine – rallies, flash mobs, protests around the world. In the physical dimension – it is your opportunity to take to the streets and declare: “No to Putin’s aggression, no to war.” There you may find information about past and future rallies in your city in support of Ukraine. This is a permanent platform for Ukrainian diaspora and people all over the world concerned about the situation in Ukraine.
So here’s a couple of things you could do yourself to help:
* if there is a political rally in your city, then participate in it and write about it on social media with geolocation and the hashtag #WorldForUkraine
* if there are no rallies nearby, organize one in support of Ukraine yourself, write about it on social media with geolocation adding the hashtag #WorldForUkraine
The map will add information about gathering by #WorldForUkraine AUTOMATICALLY
Your voice now stronger THAN ever
All rallies are already here: https://worldforukraine.net
Opinion
Russia And Ukraine At The Beginning of 2022

This opinion piece was written by Dr. Nicholas Dima. Dr. Dima was formerly a Professor of Geography and Geopolitics at Djibouti University, St. Mary’s University College and James Madison University. From 1975 to 1985 and from 1989 to 2001, Dr. Dima was a Writer and Field Reporter at Voice of America. The opinion does not necessarily represent the opinion of the editorial staff of Moldova.org.
***
The 21st Century Russian Federation is a rebirth of the 19-th Century Tsarist Empire; a huge territory inhabited by hundreds of ethnic groups held together by an authoritarian government. Having acquired a diversity of lands and peoples that would not freely want to be together, Moscow has to be on guard. It has to keep an eye on those who are inside the federation and to make sure that no outsiders threaten its territory. Otherwise, in a nutshell, Ukraine is Russia’s biggest dilemma and Russia is Ukraine’s biggest nightmare!
In 1991 Moscow agreed reluctantly to the dissolution of the former USSR. Ukraine became independent and consented to give up its nuclear arsenal inherited from the Soviet Union in exchange for territorial guaranties. Russia did not keep its engagement. It violated the Minsk protocol and in 2014, after a hybrid war, annexed Crimea. At the same time, pro-Russian forces took over two important eastern Ukrainian regions, Lugansk and Donetsk, where the population is ethnically mixed and somehow pro-Russian.
Since the annexation of Crimea, Moscow has strengthened its military presence in the peninsula and in the Black and Azov Seas. Furthermore, it built a strategic bridge that connects Crimea with the Russian mainland. Then, Russia began to reject NATO activities in East Europe and to denounce the presence of the US Navy in the Black Sea as provocations. In order to counter NATO, Russia also brought some of its warships from the Caspian Sea to the Black Sea through the Volga-Don Canal.
During recent years, Ukraine approached the United States and NATO and asked for assistance and, eventually, for membership in the EU and possibly NATO. For Moscow, however, Ukraine is an essential buffer zone against the West. With President Vladimir Putin lamenting the dismemberment of the USSR and embracing the traditional Russian expansionist mentality, the perspective of Ukraine’s NATO membership would be an existential threat.
The current situation at the Russo-Ukrainian border is tense and the stakes are high. Neither country is satisfied with the status quo, but the choices are very risky. The important Donbas region of East Ukraine, controlled by pro-Russian forces, is in a limbo. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky is losing support among the people and must defend his country’s integrity. Currently, Putin has the upper hand and military superiority on his side, but using brute force in the conflict could trigger further Western economic sanctions and even military hostility.
For now it seems that Moscow is mainly posturing, but the true Russian intentions are not clear. Thus, a miscalculation could trigger a catastrophe of international proportions. No one knows how the events will play out, but the danger is obvious. Moscow is playing with fire. Apparently, it does not want a full war, neither the current stalemate, nor a retreat. What does it want? It seems that Moscow knows what it wants, but not necessarily what it can!
Regionally, the situation between Europe and Russia is complex and internationally the world is confronted with threatening new realignments. With the help of Russia, Belarus has encouraged thousand of Middle East migrants to assail the Polish border and the European Union. Poland has mobilized its forces and NATO and EU are on alert. The three Baltic countries also feel threatened. And the recent Russo-Chinese economic cooperation and military rapprochement reinforce the international apprehension.
Since the dissolution of the USSR, Russia went through several uneasy stages. During the first years of transition toward a new political system Russia experienced economic decline and popular unrest. Then, Putin took over and managed to stabilize the country. Russia opted for security and stability instead of political democracy and economic prosperity. At the same time, Kremlin focused its resource on the military and strengthened Russia’s war capacity.
For the time being, Russia may want to perpetuate the current situation and to keep Ukraine under its thumb. However, things are not static and sometimes they move unpredictably. What if Ukraine does become a NATO member? Then, it will be impossible for Russia to challenge Kyiv without triggering a devastating war. On the other hand, waiting is not in Russia’s advantage. Demographically, ethnic Russians are declining and the non-Russians, mostly Muslims, are fast increasing. The continuous emigration to the West of many Russians is not helping the population balance either. This trend will almost certainly renew old conflicts especially in the unsettled Caucasus region…
Attacking Ukraine now, overtly or through a hybrid war, would be risky for Russia and would not bring a lasting solution to the dispute. The war could destabilize Kyiv and even dismember Ukraine, but it would also destabilize the Russian Federation. The present tension will probably be diffused, but the next time around, in about 10 to 20 years, Putin will be gone, Moscow itself will be in disarray, Caucasian Muslims will be asking openly for independence and Ukraine will be ready and capable to fight Russia.
A Russo-Ukrainian war, now or later, will immediately have regional effects engaging Belarus and most likely Poland, the Baltic States, Moldova, Romania and implicitly NATO. Romania, for example, will follow its western allies, but it could not ignore the fact that certain formerly Romanian lands are now part of Ukraine. As for Moldova, beyond the facts that Moldovans are Romanians, its Transnistrian (Transdnestr) area is entirely under Russian control and in an eventual war will be used by Moscow against Ukraine.
Nicholas Dima, January 1, 2022
Culture
The village of the first astronomer in the Republic of Moldova