Politics
Russian air defense weakness: modernizing or optimizing?
Reading Time: 4 minutesViktor Ozerov, the Chairman of the Defense Committee of the Russian Federation Council, suggested during the recent operational-strategic exercise, Vostok 2010, that the key task is to provide the armed forces with “advanced weapons and military hardware.”
by Roger McDermott
Viktor Ozerov, the Chairman of the Defense Committee of the Russian Federation Council, suggested during the recent operational-strategic exercise, Vostok 2010, that the key task is to provide the armed forces with “advanced weapons and military hardware.” Ozerov claimed that the first stage in Defense Minister, Anatoliy Serdyukov’s, reform has been completed, namely the creation of “100 percent permanent readiness units, as well as “the first steps to equip them with new state-of-the-art weapons and military hardware. Now we need to make sure that this new structure functions effectively” (Interfax, July 7).
While such claims are increasingly commonplace, as authorities shore up support for the defense reform, the challenge presented by re-equipping the armed forces remains underestimated at the very highest levels of government. This is illustrated by problems linked to the unified system of state identification used by the Russian armed forces and security structures: the radar beacon transponders of the Parol (password) system (Yedinaya Systema Gosudarstvennogo Radiolokatsionnogo Opoznavaniya –YeSGRLO). This also applies to the CIS member countries that signed the 1992 Minsk Agreement (Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Ukraine and Russia). It is the Russian equivalent of the Mk XII Identification, Friend or Foe (IFF) system used by the US and NATO. Its characteristics and need for development have been actively assessed in the Russian military press (Vozdushno Kosmicheskaya Oborona No. 1, 2007, No. 3, 2009).
IFF issues were brought sharply into focus in the aftermath of the Russia-Georgia war in August 2008, as the Russian military assessed operational lessons drawn from the conflict. A notable element, based on the mutual absence of identification equipment, witnessed Russian air force ground attack aviation using onboard armaments against Russian columns, and consequently, air defense subunits in the ground forces and airborne troops fired on their own aviation. As one Russian military analyst laconically observed: “Unintentional firing of surface to air missiles (SAM’s) on one’s own military assets strongly affects the morale and psychological status of personnel” (Vozdushno Kosmicheskaya Oborona, December 5, 2009; Nezavisimoye Voyennoye Obozreniye, September 19, 2008). Moreover, Osa-AKM combat vehicles and Buk-M1 self-propelled air defense systems captured by Russian troops were equipped with standard ground radar interrogators (without the encoding units that guarantee the proper operation of the equipment), which enabled them to identify air targets in non-guaranteed mode, determining the position and affiliation of Russian air force aviation within one minute; Georgian air defense crews could, therefore, launch SAM’s to the limits of the missile range.
Despite the reforms conducted since then, and the target to modernize equipment, Russian air defense subunits operating within combined-arms units do not possess ground based radio interrogators (nazemnyy radiolokatsionnyy zaproschik –NRZ) of the Parol system, nor are armored command vehicles used by the commanders of battalions and above equipped with radar beacon transponders of this system. Russian air force pilots, in the absence of the necessary equipment, identify ground-based assets using the archaic method of looking at orange smoke and forward aviation spotters in combined-arms units using voice over radio. Additionally, pilots fail to use identification signals and ground troops often lack sufficient training in the visual identification of aircraft.
The shortcomings of the state identification system are magnified by the lack of a federal agency that might coordinate the relevant activities among the ministries and departments involved. There is no legal framework regulating the domestic development and use of a state identification system, or in coordination with allied states (apart from Belarus) or other foreign countries in accordance with international agreements. The Parol system also suffers at a technical level, due to dwindling spare parts and accessories for maintenance of the equipment within the military. Every unit of encoding equipment, for instance, requires technical maintenance and periodic repair to ensure its continued functioning (Vozdushno Kosmicheskaya Oborona, December 5, 2009).
Air force and air defense reorganization has occurred three times since the collapse of the Soviet Union. In 1992 they decreased fivefold, in 1997 by 2.5 times, and after the latest “optimization” is complete, it will mark an additional twofold decline. Air defense formations will be converted into aerospace defense brigades and air divisions into first-category air bases (air regiments will form second category air bases). Second category air bases will replace the regiment of two squadrons with one: the main tactical unit will be a single squadron of 12-16 aircraft. The aerospace defense brigade in Rostov-on-Don will have one air base. Instead of four air regiments, it will have three air squadrons. It appears the numbers of squadrons is being determined by the level of technical serviceability and reduction of the officer corps (Vozdushno Kosmicheskaya Oborona, November 21, 2009).
The factors determining the requirements for ensuring the state’s security, including military security, were encapsulated in the National Security Strategy signed by President, Dmitry Medvedev, on May 12, 2009 (www.scrf.gov.ru, May 12, 2009). On that same day, he also signed Edict 536 on “The Principles of Strategic Planning in the Russian Federation,” which serves to guide the military-political leadership in formulating national security policy. An annex to this document also specified national security criteria and indicators used in estimating Russian national security (Krasnaya Zvezda, March 5; Vremya Novostey, December 11, 2009; Vozdushno Kosmicheskaya Oborona, November 21, 2009; Aerokosmicheskiy Kuryer, November 11, 2009; Stoletiye, November 10, 2009). In the military, however, only three indicators are used in estimating the combat potential of the armed forces:
1. The percentage of permanent readiness units in the table of organization and equipment.
2. The numbers of modern models of arms and equipment (represented as a percentage of the overall arms and equipment inventory.
3. The strength level of military and engineering cadres (percentage of leadership personnel with higher military and higher special engineering-technical education among the overall number of leadership personnel).
It is unclear how Russian defense planners correlate this to the capabilities of “hypothetical enemies” on strategic axes, or whether they have clear estimates on the number of formations needed, type and how they should be distributed. The technical demands involved in modernizing the air force and air defense forces are acute, and will require sustained investment and political willingness to resolve over a longer timeframe than the government is currently willing to admit. Consequently, future Russian military operations, including those conducted jointly within the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO), would almost certainly risk high levels of “friendly fire” causalities.
Featured
FC Sheriff Tiraspol victory: can national pride go hand in hand with political separatism?
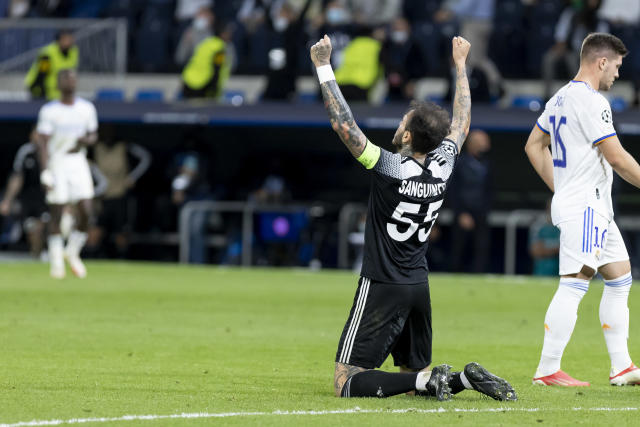

A new football club has earned a leading place in the UEFA Champions League groups and starred in the headlines of worldwide football news yesterday. The Football Club Sheriff Tiraspol claimed a win with the score 2-1 against Real Madrid on the Santiago Bernabeu Stadium in Madrid. That made Sheriff Tiraspol the leader in Group D of the Champions League, including the football club in the groups of the most important European interclub competition for the first time ever.
International media outlets called it a miracle, a shock and a historic event, while strongly emphasizing the origin of the team and the existing political conflict between the two banks of the Dniester. “Football club from a pro-Russian separatist enclave in Moldova pulls off one of the greatest upsets in Champions League history,” claimed the news portals. “Sheriff crushed Real!” they said.
Moldovans made a big fuss out of it on social media, splitting into two groups: those who praised the team and the Republic of Moldova for making history and those who declared that the football club and their merits belong to Transnistria – a problematic breakaway region that claims to be a separate country.
Both groups are right and not right at the same time, as there is a bunch of ethical, political, social and practical matters that need to be considered.
Is it Moldova?
First of all, every Moldovan either from the right or left bank of Dniester (Transnistria) is free to identify himself with this achievement or not to do so, said Vitalie Spranceana, a sociologist, blogger, journalist and urban activist. According to him, boycotting the football club for being a separatist team is wrong.
At the same time, “it’s an illusion to think that territory matters when it comes to football clubs,” Spranceana claimed. “Big teams, the ones included in the Champions League, have long lost their connection both with the countries in which they operate, and with the cities in which they appeared and to which they linked their history. […] In the age of globalized commercial football, teams, including the so-called local ones, are nothing more than global traveling commercial circuses, incidentally linked to cities, but more closely linked to all sorts of dirty, semi-dirty and cleaner cash flows.”
What is more important in this case is the consistency, not so much of citizens, as of politicians from the government who have “no right to celebrate the success of separatism,” as they represent “the national interests, not the personal or collective pleasures of certain segments of the population,” believes the political expert Dionis Cenusa. The victory of FC Sheriff encourages Transnistrian separatism, which receives validation now, he also stated.
“I don’t know how it happens that the “proud Moldovans who chose democracy”, in their enthusiasm for Sheriff Tiraspol’s victory over Real Madrid, forget the need for total and unconditional withdrawal of Russian troops from Transnistria!” declared the journalist Vitalie Ciobanu.
Nowadays, FC Sheriff Tiraspol has no other choice than to represent Moldova internationally. For many years, the team used the Moldovan Football Federation in order to be able to participate in championships, including international ones. That is because the region remains unrecognised by the international community. However, the club’s victory is presented as that of Transnistria within the region, without any reference to the Republic of Moldova, its separatist character being applied in this case especially.
Is it a victory?
In fact, FC Sheriff Tiraspol joining the Champions League is a huge image breakthrough for the Transnistrian region, as the journalist Madalin Necsutu claimed. It is the success of the Tiraspol Club oligarchic patrons. From the practical point of view, FC Sheriff Tiraspol is a sports entity that serves its own interests and the interests of its owners, being dependent on the money invested by Tiraspol (but not only) oligarchs.
Here comes the real dilemma: the Transnistrian team, which is generously funded by money received from corruption schemes and money laundering, is waging an unequal fight with the rest of the Moldovan football clubs, the journalist also declared. The Tiraspol team is about to raise 15.6 million euro for reaching the Champions League groups and the amounts increase depending on their future performance. According to Necsutu, these money will go directly on the account of the club, not to the Moldovan Football Federation, creating an even bigger gab between FC Sheriff and other football clubs from Moldova who have much more modest financial possibilities.
“I do not see anything useful for Moldovan football, not a single Moldovan player is part of FC Sheriff Tiraspol. I do not see anything beneficial for the Moldovan Football Federation or any national team.”
Is it only about football?
FC Sheriff Tiraspol, with a total estimated value of 12.8 million euros, is controlled by Victor Gusan and Ilya Kazmala, being part of Sheriff Holding – a company that controls the trade of wholesale, retail food, fuels and medicine by having monopolies on these markets in Transnistria. The holding carries out car trading activities, but also operates in the field of construction and real estate. Gusan’s people also hold all of the main leadership offices in the breakaway region, from Parliament to the Prime Minister’s seat or the Presidency.
The football club is supported by a holding alleged of smuggling, corruption, money laundering and organised crime. Moldovan media outlets published investigations about the signals regarding the Sheriff’s holding involvement in the vote mobilization and remuneration of citizens on the left bank of the Dniester who participated in the snap parliamentary elections this summer and who were eager to vote for the pro-Russian socialist-communist bloc.
Considering the above, there is a great probability that the Republic of Moldova will still be represented by a football club that is not identified as being Moldovan, being funded from obscure money, growing in power and promoting the Transnistrian conflict in the future as well.
Photo: unknown
Politics
Prime Minister Natalia Gavrilita meets high-ranking EU officials in Brussels

Prime Minister of the Republic of Moldova, Natalia Gavrilita, together with Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs, Nicu Popescu, pay an official visit to Brussels, between September 27-28, being invited by High Representative of the European Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy, Josep Borrell Fontelles.
Today, Prime Minister had a meeting with Charles Michel, President of the European Council. The Moldovan PM thanked the senior European official for the support of the institution in strengthening democratic processes, reforming the judiciary and state institutions, economic recovery and job creation, as well as increasing citizens’ welfare. Natalia Gavrilita expressed her confidence that the current visit laid the foundations for boosting relations between the Republic of Moldova and the European Union, so that, in the next period, it would be possible to advance high-level dialogues on security, justice and energy. Officials also exchanged views on priorities for the Eastern Partnership Summit, to be held in December.
“The EU is open to continue to support the Republic of Moldova and the ambitious reform agenda it proposes. Moldova is an important and priority partner for us,” said Charles Michel.
Prime Minister Natalia Gavrilita also met with Paolo Gentiloni, European Commissioner for Economy, expressing her gratitude for the support received through the OMNIBUS macro-financial assistance program. The two officials discussed the need to advance the recovery of money from bank fraud, to strengthen sustainable mechanisms for supporting small and medium-sized enterprises in Moldova, and to standardize the customs and taxes as one of the main conditions for deepening cooperation with the EU in this field.
Additionally, Prime Minister spoke about the importance of the Eastern Partnership and the Deep Free Trade Agreement, noting that the Government’s policies are aimed at developing an economic model aligned with the European economic model, focused on digitalization, energy efficiency and the green economy.
A common press release of the Moldovan Prime Minister with High Representative of the European Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy/Vice-President of the Commission, Josep Borrell Fontelles, took place today, where the agenda of Moldova’s reforms and the main priorities to focus on in the coming months were presented: judiciary reform; fighting COVID-19 pandemic; promoting economic recovery and conditions for growth and job creation; strengthening state institutions and resilience of the country.
“I am here to relaunch the dialogue between my country and the European Union. Our partnership is strong, but I believe there is room for even deeper cooperation and stronger political, economic and sectoral ties. I am convinced that this partnership is the key to the prosperity of our country and I hope that we will continue to strengthen cooperation.”
The Moldovan delegation met Didier Reynders, European Commissioner for Justice. Tomorrow, there are scheduled common meetings with Oliver Varhelyi, European Commissioner for Neighborhood and Enlargement, Adina Valean, European Commissioner for Transport and Kadri Simson, European Commissioner for Energy.
Prime Minister will also attend a public event, along with Katarina Mathernova, Deputy Director-General for Neighbourhood Policy and Enlargement Negotiations.
Photo: gov.md
Politics
Promo-LEX about Maia Sandu’s UN speech: The president must insist on appointing a rapporteur to monitor the situation of human rights in Transnistria
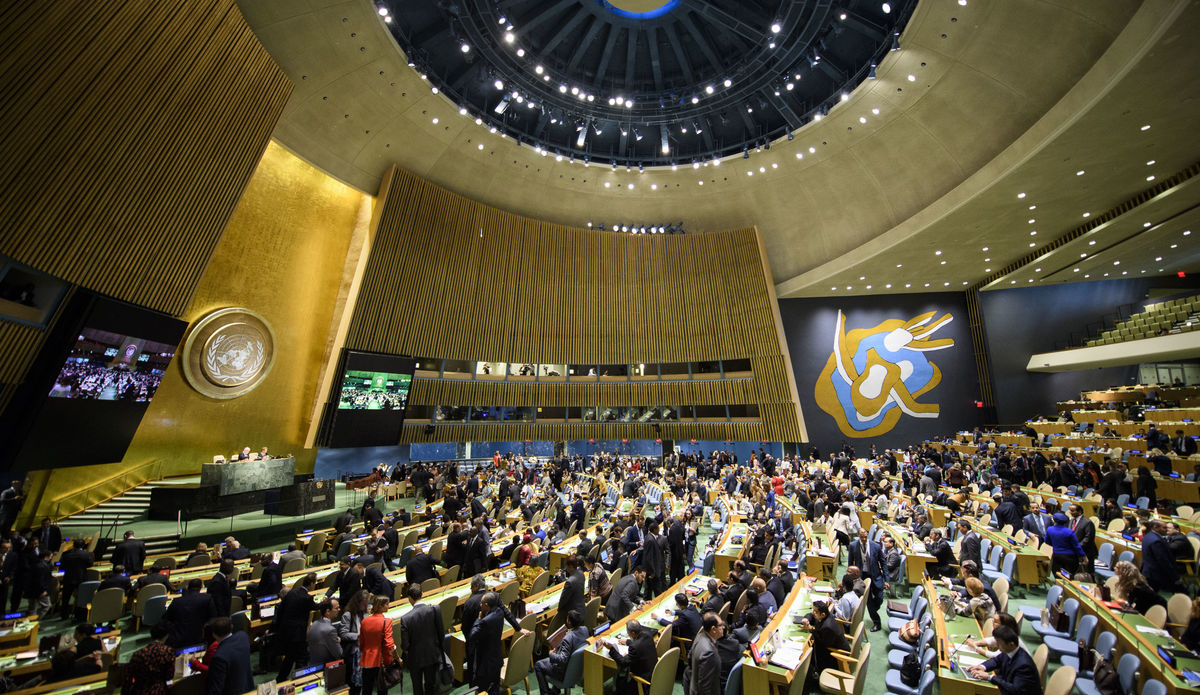

The President of the Republic of Moldova, Maia Sandu, pays an official visit to New York, USA, between September 21-22. There, she participates in the work of the United Nations General Assembly. According to a press release of the President’s Office, the official will deliver a speech at the tribune of the United Nations.
In this context, the Promo-LEX Association suggested the president to request the appointment of a special rapporteur in order to monitor the situation of human rights in the Transnistrian region. According to Promo-LEX, the responsibility for human rights violations in the Transnistrian region arises as a result of the Russian Federation’s military, economic and political control over the Tiraspol regime.
“We consider it imperative to insist on the observance of the international commitments assumed by the Russian Federation regarding the withdrawal of the armed forces and ammunition from the territory of the country,” the representatives of Promo-LEX stated. They consider the speech before the UN an opportunity “to demand the observance of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights by the Russian Federation with reference to this territory which is in its full control.”
“It is important to remember about the numerous cases of murder, torture, ill-treatment, forced enlistment in illegal military structures, the application of pseudo-justice in the Transnistrian region, all carried out under the tacit agreement of the Russian Federation. These findings stem from dozens of rulings and decisions issued by the European Court of Human Rights, which found that Russia is responsible for human rights violations in the region.”
The association representatives expressed their hope that the president of the country would give priority to issues related to the human rights situation in the Transnistrian region and would call on relevant international actors to contribute to guaranteeing fundamental human rights and freedoms throughout Moldova.
They asked Maia Sandu to insist on the observance of the obligation to evacuate the ammunition and the military units of the Russian Federation from the territory of the Republic of Moldova, to publicly support the need for the Russian Federation to implement the ECtHR rulings on human rights violations in the Transnistrian region, and to request the appointment of an UN Human Rights Council special rapporteur to monitor the human rights situation in the Transnistrian region of the Republic of Moldova.
**
The Promo-LEX Association concluded that 14 out of 25 actions planned within the National Action Plan for the years 2018–2022 concerning respecting human rights in Transnistria were not carried out by the responsible authorities.
The association expressed its concern and mentioned that there are a large number of delays in the planned results. “There is a lack of communication and coordination between the designated institutions, which do not yet have a common vision of interaction for the implementation of the plan.”
Promo-LEX requested the Government of the Republic of Moldova to re-assess the reported activities and to take urgent measures, “which would exclude superficial implementation of future activities and increase the level of accountability of the authorities.”
Photo: peacekeeping.un.org